Becoming a lawyer involves significant investment, but understanding the costs can help you plan effectively. At internetlawyers.net, we provide resources to navigate these expenses and connect with legal professionals. Earning a law degree can be attainable with careful planning and financial strategies. Let’s delve into tuition expenses, living costs, and alternative routes for prospective lawyers.
Table of Contents
- What Factors Influence the Cost of Becoming a Lawyer?
- What Is the Average Cost of Law School Tuition?
- How Much Does Law School Cost Per Year?
- What Are the Living Expenses While Attending Law School?
- How Much Does Law School Cost in Total?
- How Do Tuition Costs Vary by Law School?
- What Are Some Alternative Legal Degrees and Their Costs?
- What Financial Aid Options Are Available for Law School?
- What Additional Costs Should I Consider When Becoming a Lawyer?
- How Can Internetlawyers.net Help You on Your Legal Journey?
- FAQ
1. What Factors Influence the Cost of Becoming a Lawyer?
The cost to become a lawyer is influenced by a variety of factors that potential law students should carefully consider. These factors span from the type of institution you choose to attend, to your lifestyle during law school, and even the state in which you study. Understanding these elements can help you create a realistic financial plan.
- Type of Law School (Public vs. Private)
Public law schools generally offer lower tuition rates, especially for in-state residents. Private law schools typically have higher tuition fees, but they may also offer more generous financial aid packages. According to educationdata.org, the tuition gap between public and private schools can be significant, reaching around $25,139 per year for in-state residents. Over the traditional three-year study, this tuition gap widens to $75,417. - In-State vs. Out-of-State Tuition
Public universities charge different tuition rates based on residency. In-state tuition is substantially lower than out-of-state tuition. For example, the University of Puerto Rico offers the least expensive tuition at $9,750 per year, while Columbia University is the most expensive at $81,292 a year. - Living Expenses
Living expenses can vary widely depending on your location. Metropolitan areas like New York City or Los Angeles will have higher costs of living compared to smaller, more rural cities. These expenses include rent, utilities, food, transportation, and personal expenses. - Conditional Scholarships
Conditional scholarships, which require students to maintain a certain GPA or class standing, can affect the overall cost. These scholarships have become less common, with only 36.7% of law schools offering them in 2022-2023, compared to 61.4% in 2011-2012. Additionally, the percentage of students losing these scholarships has decreased from 36.1% in 2011-2012 to 26.5% in 2022-2023. - Bar Exam and Licensing Fees
After graduating from law school, you must pass the bar exam to become a licensed attorney. The cost of the bar exam varies by state, but it generally includes application fees, study materials, and preparation courses. The average cost of a multi-state bar exam is expected to be $160 in 2024, up from $150 in 2023. - Application Fees
Applying to law school involves application fees, which can add up quickly. The average application fee is around $80, and applicants often apply to multiple schools to increase their chances of acceptance. Applying to 5 to 15 law schools can cost between $400 and $1200 in application fees alone. - Personal Spending Habits
Your personal spending habits also play a role in the overall cost. Managing your budget effectively, seeking affordable housing options, and minimizing unnecessary expenses can help reduce your financial burden during law school.
By considering these factors, prospective law students can develop a comprehensive understanding of the financial implications of pursuing a legal education.
 Students in a law library, studying together
Students in a law library, studying together
2. What Is the Average Cost of Law School Tuition?
The average cost of law school tuition varies depending on whether you attend a public or private institution. Public schools are generally more affordable, especially if you are a resident of the state.
- Average Total Tuition
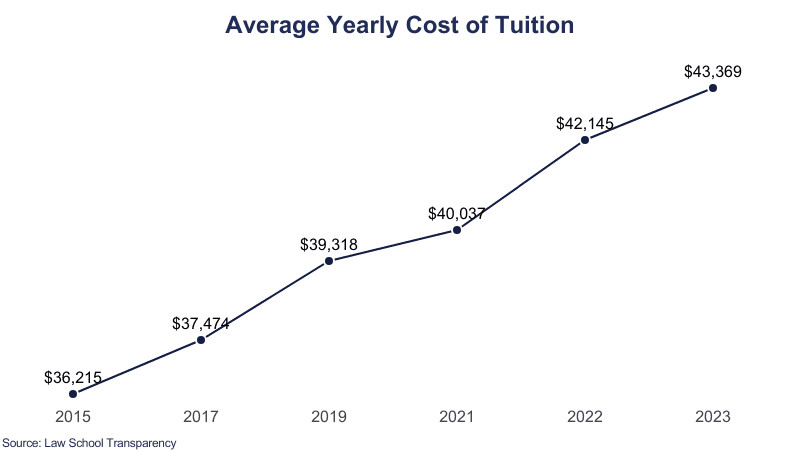
According to recent data, the average total cost of tuition alone for law school is $151,072, or $50,357 per year. This represents an increase of $1,488 between 2022 and 2023, indicating a rising trend in law school tuition costs. - Public vs. Private Schools
Tuition at public law schools is typically lower for in-state residents compared to private law schools. For example, in-state tuition at a public law school might average around $40,000 per year, while private law schools can easily exceed $60,000 or even $80,000 per year. - Historical Trends
Historically, the cost of tuition has been on the rise. Since 2011, tuition has increased by an average of $4,867 every five years. Data since the 1970s shows that tuition has increased at all ABA-accredited law schools. Experts attribute this rise to factors such as declines in student-faculty ratios, increases in faculty salaries, the development of legal clinics for practical education, the growth of administrative staff, and expansive school construction projects. - Projected Future Costs
If the current trend continues, the average yearly cost of tuition is projected to be $51,193 for the 2024-2025 school year and $53,230 for the 2025-2026 school year. This means that prospective law students should anticipate further increases in tuition costs. - Specific Examples
To illustrate the increasing tuition rates, consider the following examples:- From 1997 to 2015, the tuition at Minnesota Law School rose from $8,923 to $41,222.
- During the same period, the tuition at Ohio State Law School increased from $6,412 to $28,577.
Understanding these average costs and historical trends can help you plan your finances and explore potential funding options.
3. How Much Does Law School Cost Per Year?
The annual cost of law school encompasses not only tuition but also various fees and expenses that can significantly impact your budget.
- Average Yearly Tuition
As mentioned earlier, the average yearly cost of tuition is approximately $50,357. This figure can vary widely based on the type of law school and your residency status. - Additional Fees
In addition to tuition, law schools often charge fees for various services and resources, such as:- Technology fees: These fees cover the cost of maintaining and upgrading the school’s technology infrastructure.
- Library fees: These fees support the law library, providing access to legal databases, journals, and other resources.
- Student activity fees: These fees fund student organizations, events, and activities.
- Health services fees: These fees provide access to on-campus health services.
- Example Breakdown
Here’s an example of how the annual cost might break down at a hypothetical law school:
| Expense | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Tuition | $50,357 |
| Technology Fee | $500 |
| Library Fee | $300 |
| Student Activity Fee | $200 |
| Health Services Fee | $400 |
| Total Annual Cost | $51,757 |
- Cost Variation by School
The actual cost can vary significantly between different law schools. For example, Columbia University has an annual tuition cost of $81,292, while the University of Puerto Rico has a much lower cost of $9,750. It’s essential to research the specific costs associated with each law school you are considering. - Impact of Residency
Residency status can also significantly impact the annual cost. Public universities typically offer lower tuition rates for in-state residents, making them a more affordable option compared to private schools or out-of-state public schools.
By understanding the breakdown of annual costs and considering the specific fees associated with different law schools, you can create a more accurate budget and plan your finances accordingly.
4. What Are the Living Expenses While Attending Law School?
Living expenses constitute a significant portion of the overall cost of attending law school. These costs include housing, food, transportation, and personal expenses, all of which can vary depending on your location and lifestyle.
- Average Living Expenses
On average, living expenses total around $79,391, or $24,464 per year. However, this figure can vary widely depending on where you live. - Housing Costs
Housing is typically the largest component of living expenses. Rent prices can vary significantly depending on the city and type of accommodation.- On-Campus Housing: Some law schools offer on-campus housing, which can be a convenient and potentially more affordable option.
- Off-Campus Housing: Renting an apartment off-campus provides more flexibility but may also be more expensive, especially in urban areas.
- Food Costs
Food costs can also add up quickly. You can save money by cooking your own meals and packing lunch instead of eating out.- Groceries: Budgeting for groceries and planning meals in advance can help control your food expenses.
- Eating Out: Limiting how often you eat at restaurants and cafes can also save you money.
- Transportation Costs
Transportation costs depend on your location and mode of transportation.- Public Transportation: Using public transportation, such as buses and trains, can be a cost-effective option in many cities.
- Car Expenses: Owning a car involves expenses such as gas, insurance, parking, and maintenance.
- Personal Expenses
Personal expenses include items such as clothing, entertainment, healthcare, and personal care products.- Budgeting: Creating a budget and tracking your spending can help you manage your personal expenses effectively.
- Discretionary Spending: Limiting discretionary spending on non-essential items can also help you save money.
- Cost Variation by School
The annual living expenses vary depending on the school and its location. For example:- Stanford University has the highest annual living expenses at $47,832.
- Oklahoma City University has the lowest annual living expenses at $12,600.
Here is a comparison of living expenses at different law schools:
| Law School | Annual Living Expenses |
|---|---|
| Stanford University | $47,832 |
| Loyola Marymount University | $41,748 |
| University of California – Berkeley | $43,198 |
| Oklahoma City University | $12,600 |
| University of Wyoming | $18,020 |
| University of New Hampshire | $17,582 |
By understanding these various components of living expenses, you can create a realistic budget and make informed decisions about where to live and how to manage your finances during law school.
5. How Much Does Law School Cost in Total?
The total cost of law school is the sum of tuition, fees, and living expenses over the course of your legal education. Understanding this figure can help you prepare for the financial commitment involved.
- Average Total Cost
The average total cost of law school is $230,163. This includes tuition, fees, and living expenses for the typical three-year Juris Doctor (J.D.) program. - Breakdown of Costs
A detailed breakdown of the average total cost includes:- Tuition: $151,072
- Living Expenses: $79,391
- Cost Variation
The total cost can vary significantly depending on several factors, including:- Type of Law School: Public vs. Private
- Residency Status: In-state vs. Out-of-state
- Location: Urban vs. Rural
- Personal Spending Habits: Budgeting and lifestyle choices
- Estimating Your Total Cost
To estimate your total cost, consider the following steps:- Research Tuition Rates: Obtain the current tuition rates for the law schools you are considering.
- Estimate Living Expenses: Research the cost of living in the cities where the law schools are located, including housing, food, transportation, and personal expenses.
- Factor in Fees: Consider any additional fees charged by the law schools, such as technology fees, library fees, and student activity fees.
- Calculate Total Cost: Add up the estimated tuition, fees, and living expenses for each year of law school to arrive at your total cost.
- Example Scenario
Let’s consider an example scenario:- Attending a public law school with in-state tuition:
- Annual Tuition: $40,000
- Annual Fees: $1,000
- Annual Living Expenses: $25,000
- Total Annual Cost: $66,000
- Total Cost for Three Years: $198,000
- Attending a private law school:
- Annual Tuition: $65,000
- Annual Fees: $1,500
- Annual Living Expenses: $30,000
- Total Annual Cost: $96,500
- Total Cost for Three Years: $289,500
- Attending a public law school with in-state tuition:
By understanding these average costs and variations, you can better prepare for the financial commitment of law school and explore potential funding options, such as scholarships, grants, and loans.
6. How Do Tuition Costs Vary by Law School?
Tuition costs can vary dramatically among different law schools. This variation depends on factors such as the school’s reputation, location, and whether it is a public or private institution.
- Range of Tuition Costs
Tuition costs can range from less than $10,000 per year at some public law schools to over $80,000 per year at elite private institutions. - Public vs. Private Institutions
Public law schools typically offer lower tuition rates for in-state residents, while private law schools tend to have higher tuition rates regardless of residency. - Geographic Location
The location of the law school can also impact tuition costs. Law schools in urban areas or states with higher costs of living may have higher tuition rates. - Examples of Tuition Costs
Here are some examples of tuition costs at different law schools:
| Law School | Annual Tuition Cost |
|---|---|
| Columbia University | $81,292 |
| New York University | $80,014 |
| University of Chicago | $77,952 |
| University of Pennsylvania | $76,934 |
| Harvard University | $75,008 |
| University of California – Berkeley | $75,031 |
| Duke University | $75,738 |
| Georgetown University | $75,950 |
| University of Puerto Rico | $9,750 |
| Southern Illinois University | $21,555 |
| Northern Illinois University | $23,553 |
| CUNY | $26,203 |
| University of Akron | $26,215 |
- Factors Influencing Tuition Costs
Several factors influence tuition costs at law schools:- Reputation and Ranking: Highly ranked law schools often charge higher tuition rates due to their prestige and demand.
- Faculty Salaries: Law schools with renowned faculty members may have higher tuition rates to cover competitive salaries.
- Resources and Facilities: Law schools that offer state-of-the-art resources, facilities, and programs may charge higher tuition rates.
- Financial Aid Policies: Law schools with generous financial aid policies may have higher tuition rates to offset the cost of scholarships and grants.
- Researching Tuition Costs
When researching law schools, it’s essential to compare tuition costs and consider the overall value of the education you will receive.
By understanding the variations in tuition costs among different law schools, you can make informed decisions and choose a law school that fits your budget and career goals.
7. What Are Some Alternative Legal Degrees and Their Costs?
For individuals interested in the legal field but not necessarily seeking to become practicing attorneys, alternative legal degrees offer a pathway to engage with the law in different capacities. These degrees, such as the Juris Master (J.M.) and Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.), are typically shorter and less expensive than a traditional Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree.
- Juris Master (J.M.)
- Overview: A J.M. degree is designed for professionals who want to gain legal knowledge without becoming lawyers. It is suitable for individuals in fields such as business, healthcare, and technology, where understanding legal principles can enhance their performance.
- Duration: Typically lasts one to two years.
- Cost: The cost of a J.M. degree varies by institution.
- Example 1: A J.M. from Florida International University is a one-year program that costs $24,726.
- Example 2: A J.M. from Liberty University School of Law costs $16,950 in tuition for the entire program.
- Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.)
- Overview: An M.L.S. degree is similar to a J.M. and provides a foundation in legal principles and concepts. It is often pursued by professionals who work in regulated industries or require a working knowledge of the law.
- Duration: Many M.L.S. degrees are offered online and can be completed within one to two years.
- Cost: The cost of an M.L.S. degree varies by institution and program format.
- Example 1: The University of Oklahoma’s M.L.S. degrees typically cost $16,995 for residents and $30,840 for non-residents.
- Example 2: Seattle University School of Law’s M.L.S. degree costs $43,860, with no price differentiation between residents and non-residents.
- Comparison of Costs
| Degree | Duration | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Juris Doctor (J.D.) | 3 years | Average total cost: $230,163 |
| Juris Master (J.M.) | 1-2 years | $16,950 – $24,726 |
| Master of Legal Studies (M.L.S.) | 1-2 years | $16,995 (residents) – $43,860 (non-residents) |
- Benefits of Alternative Degrees
- Shorter Duration: J.M. and M.L.S. programs typically take less time to complete than a J.D. program.
- Lower Cost: These degrees are generally less expensive than a J.D., reducing the financial burden on students.
- Career Advancement: These degrees can enhance career prospects for professionals in various fields by providing them with legal knowledge and skills.
- Considerations
- Career Goals: Consider your career goals and whether a J.D. is necessary for your desired path.
- Program Focus: Research the curriculum and focus of different J.M. and M.L.S. programs to ensure they align with your interests and career objectives.
- Accreditation: Verify the accreditation of the program and institution to ensure the quality of the education.
By exploring alternative legal degrees, individuals can gain valuable legal knowledge and skills without the extensive time and financial commitment required for a J.D. degree.
8. What Financial Aid Options Are Available for Law School?
Financing a law school education can be a significant challenge, but numerous financial aid options are available to help students manage the costs. These options include scholarships, grants, loans, and work-study programs.
- Scholarships
- Merit-Based Scholarships: Awarded based on academic achievement, LSAT scores, and other qualifications.
- Need-Based Scholarships: Awarded based on financial need, as determined by the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA).
- Conditional Scholarships: Awarded to students who maintain a certain GPA or class standing. However, these scholarships have decreased in popularity, with only 36.7% of law schools offering them in 2022-2023, compared to 61.4% in 2011-2012.
- Diversity Scholarships: Aimed at increasing diversity in the legal profession by supporting students from underrepresented backgrounds.
- Grants
- Federal Grants: Such as the Pell Grant, are typically awarded based on financial need and do not need to be repaid.
- Institutional Grants: Offered by law schools themselves, these grants can cover a portion or the full cost of tuition. In 2018, 6% of law school students received institutional grants paying the full cost of their tuition, while 28% received grants paying off at least half the cost.
- Loans
- Federal Loans: Offered by the U.S. Department of Education, including Direct Unsubsidized Loans and Direct Graduate PLUS Loans. These loans typically have fixed interest rates and various repayment options.
- Private Loans: Offered by banks and other financial institutions. Private loans may have variable or fixed interest rates and different repayment terms.
- Work-Study Programs
- Federal Work-Study: Provides part-time jobs for students with financial need, allowing them to earn money to help pay for their education.
- Law School Employment: Some law schools offer on-campus employment opportunities, such as research assistant positions or library jobs.
- Financial Aid Trends
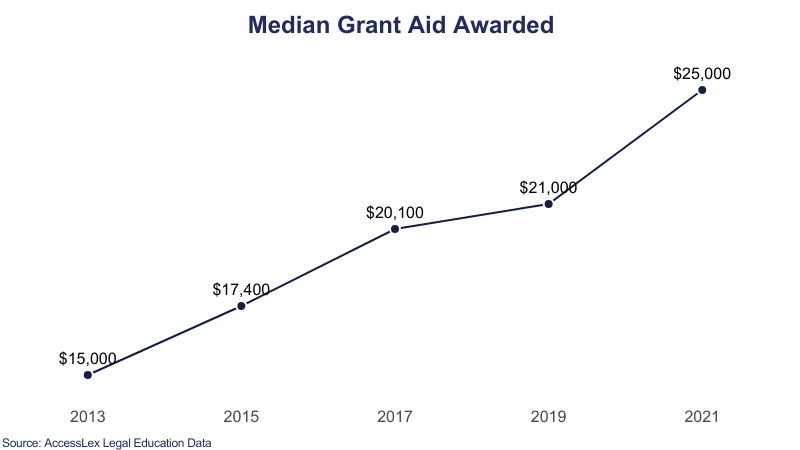
- Median Grant Aid: Between 2013 and 2021, the median grant aid awarded to full-time students increased by $7,500, indicating a growing commitment to supporting law students financially.
- Debt Statistics
- Student Loan Debt: It’s important to be aware of the potential for accumulating debt. In 2016, 69% of law school graduates took out loans, and the average cumulative debt held by those who completed law degrees was $145,500.
- Tips for Securing Financial Aid
- Apply Early: Submit your FAFSA and scholarship applications as early as possible to maximize your chances of receiving aid.
- Research Scholarships: Look for scholarships offered by law schools, bar associations, and other organizations.
- Compare Loan Options: Carefully compare the interest rates, fees, and repayment terms of different loan options before making a decision.
- Create a Budget: Develop a realistic budget to track your expenses and manage your finances effectively.
By exploring these financial aid options and following these tips, you can reduce the financial burden of law school and achieve your educational goals.
 Student reviewing financial aid documents
Student reviewing financial aid documents
9. What Additional Costs Should I Consider When Becoming a Lawyer?
Beyond tuition and living expenses, several additional costs are associated with becoming a lawyer. These costs include application fees, bar exam fees, and professional development expenses.
- Law School Application Fees
- Average Cost: Law school application fees typically cost around $80 per school.
- Multiple Applications: The average applicant applies to 5 to 15 law schools, resulting in $400 to $1200 in application fees.
- Bar Exam Fees
- Bar Exam Cost: The average cost of a multi-state bar exam is expected to be $160 in 2024, up from $150 in 2023.
- Preparation Courses: Many students enroll in bar preparation courses, which can cost several thousand dollars.
- Licensing and Admission Fees
- State Bar Admission: After passing the bar exam, you must pay licensing and admission fees to practice law in your state.
- Professional Development Expenses
- Professional Attire: Investing in professional attire for interviews, internships, and networking events.
- Networking Events: Attending legal conferences, seminars, and networking events.
- Professional Memberships: Joining bar associations and other professional organizations.
- Technology and Resources
- Laptop and Software: Purchasing a reliable laptop and necessary software for coursework and legal research.
- Legal Research Databases: Subscribing to legal research databases such as LexisNexis or Westlaw.
- Health Insurance
- Health Coverage: Ensuring you have adequate health insurance coverage throughout law school.
- Personal Expenses
- Miscellaneous Costs: Covering personal expenses such as transportation, entertainment, and unexpected costs.
- Debt Management
- Interest on Loans: Accounting for the interest that accrues on student loans during law school and the repayment period.
- Summary of Additional Costs
| Expense | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Law School Application Fees | $400 – $1200 |
| Bar Exam Fees | $160+ |
| Bar Preparation Courses | $1,000 – $4,000 |
| Licensing and Admission Fees | Varies by State |
| Professional Attire | $500 – $1,000 |
| Networking Events | $200 – $500+ |
| Professional Memberships | $100 – $500+ |
| Laptop and Software | $1,000 – $2,000 |
| Legal Research Databases | $50 – $100+ per month |
| Health Insurance | Varies by Plan |
| Personal Expenses | Varies |
| Total Estimated Additional Costs | $3,310 – $11,760+ |
By considering these additional costs, you can develop a comprehensive budget and plan your finances accordingly.
10. How Can Internetlawyers.net Help You on Your Legal Journey?
Navigating the legal landscape can be complex, but internetlawyers.net is here to simplify the process and provide you with the resources you need. Whether you’re seeking legal information, looking for a qualified attorney, or need guidance on legal processes, our platform offers a wealth of support.
-
Comprehensive Legal Information
- Extensive Resource Library: Access a wide range of articles, guides, and resources covering various areas of law.
- Expert Insights: Benefit from insights provided by experienced legal professionals.
-
Finding the Right Attorney
- Attorney Directory: Search our directory to find attorneys specializing in your area of need.
- Detailed Profiles: Review attorney profiles to learn about their qualifications, experience, and areas of expertise.
-
Understanding Legal Processes
- Step-by-Step Guides: Navigate complex legal processes with clear, step-by-step guides.
- Legal Terminology: Understand common legal terms with our easy-to-understand glossary.
-
Connecting with Legal Professionals
- Direct Contact: Connect with attorneys directly through our platform to discuss your legal needs.
- Personalized Recommendations: Receive personalized recommendations for attorneys based on your specific situation.
-
Additional Resources
- Legal News and Updates: Stay informed about the latest legal news, trends, and developments.
- Tools and Templates: Access helpful legal tools and templates to assist you with various tasks.
-
Success Stories
- Real-Life Examples: Learn from the experiences of others through real-life success stories and case studies.
-
Contact Information
For further assistance, you can reach us at:
- Address: 111 Broadway, New York, NY 10006, United States
- Phone: +1 (212) 555-1212
- Website: internetlawyers.net
-
Take Action
Visit internetlawyers.net today to explore our resources, find an attorney, and take the first step towards resolving your legal matters. Let us help you navigate the legal system with confidence and ease.
11. FAQ
- Is law school tuition tax deductible?
While you can’t deduct tuition expenses directly, you may be able to claim the Lifetime Learning Credit for qualified tuition and related expenses. Additionally, the interest you pay on student loans may be tax deductible. Consult a tax professional for personalized advice. - How can I reduce law school costs?
Consider attending a public law school, living frugally, applying for scholarships and grants, and working part-time to offset expenses. - What is the LSAT, and how does it affect my chances of getting scholarships?
The Law School Admission Test (LSAT) is a standardized test required for admission to most law schools. A high LSAT score can significantly improve your chances of receiving merit-based scholarships. - Are there scholarships specifically for minority students?
Yes, many scholarships are specifically targeted toward minority students to promote diversity in the legal profession. Research and apply for these scholarships to increase your chances of receiving financial aid. - How do conditional scholarships work?
Conditional scholarships require students to maintain a certain GPA or class standing to continue receiving the scholarship. If you fail to meet the conditions, you may lose the scholarship. - What are the best ways to prepare for the bar exam?
Enroll in a comprehensive bar preparation course, create a study schedule, practice with sample questions, and seek guidance from experienced attorneys. - What is the difference between a J.D., J.M., and M.L.S. degree?
A J.D. (Juris Doctor) is the traditional law degree required to become a practicing attorney. A J.M. (Juris Master) and M.L.S. (Master of Legal Studies) are alternative degrees for professionals who want legal knowledge without becoming lawyers. - Can I work while attending law school?
Yes, many students work part-time while attending law school. However, it’s important to balance work with your studies to avoid burnout and maintain good academic standing. - How do I choose the right law school for me?
Consider factors such as tuition costs, location, reputation, faculty, and program offerings. Visit the law schools you are interested in and talk to current students and faculty members. - What is the job market like for lawyers?
The job market for lawyers can vary depending on the location and area of practice. Research the job market in your desired location and network with attorneys to learn about employment opportunities.

