The average lawyer has around $130,000 in student loan debt, a significant financial consideration when pursuing a legal career. At internetlawyers.net, we aim to provide essential insights into managing law school debt, offering solutions for prospective and current legal professionals. Understanding loan forgiveness programs, debt consolidation, and financial planning can empower you to navigate your legal journey with greater confidence.
1. What is the Average Student Loan Debt for Law School Graduates?
The average student loan debt for law school graduates is approximately $130,000. This substantial debt load is a significant concern for many aspiring lawyers, impacting their financial decisions and career paths. According to Education Data Initiative, 71% of law school students graduate with debt, highlighting how common it is to borrow for legal education.
Expanding on Law School Debt Statistics
The $130,000 figure represents the average debt accumulated by law school graduates, combining loans taken out for law school and potentially for prior undergraduate education. The amount can vary significantly based on several factors, including the school attended, the availability of scholarships and grants, and the student’s personal financial situation.
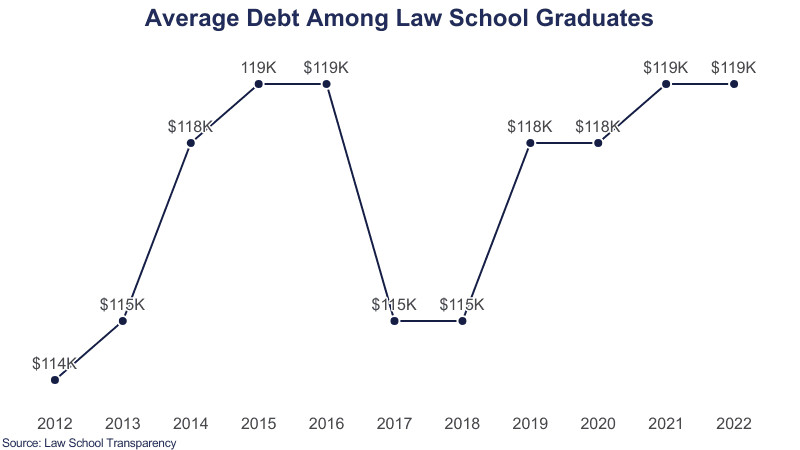 Average Law School Debt 2024 2 on Education Data Initiative
Average Law School Debt 2024 2 on Education Data Initiative
Factors Influencing Law School Debt
- Tuition Costs: Law school tuition can range from relatively affordable at public institutions to very expensive at private and top-tier schools.
- Living Expenses: The cost of living in the city where the law school is located can also significantly impact the total amount borrowed.
- Financial Aid: Scholarships, grants, and family contributions can reduce the amount needed to be borrowed.
- Interest Rates: The interest rates on student loans will affect the total repayment amount over time.
2. How Does Law School Debt Compare to Other Graduate Degrees?
Law school debt is generally higher than the debt for many other graduate degrees. The extensive duration of law school (typically three years) and the high tuition costs contribute to this difference. Medical school graduates, for instance, often have similar or higher debt levels, but their earning potential is also typically higher.
Detailed Comparison of Debt Across Graduate Programs
| Degree Type | Average Debt | Potential Income |
|---|---|---|
| Law School | $130,000 | $57,500 (Public Sector) – $200,000 (Private Sector) |
| Medical School | $200,000+ | $200,000 – $300,000+ |
| Business School | $80,000+ | $100,000 – $150,000+ |
| Engineering School | $50,000+ | $70,000 – $120,000+ |
| Education | $40,000+ | $40,000 – $70,000+ |
Reasons for Higher Law School Debt
- Longer Program Length: Law school is typically a three-year full-time program, whereas some master’s programs can be completed in one or two years.
- Higher Tuition Rates: Many law schools, particularly private institutions, have high tuition rates.
- Opportunity Cost: Students forgo full-time employment for three years, missing out on potential earnings.
3. What Impact Does Law School Debt Have on Career Choices?
A substantial number of law school graduates, 26%, prioritize jobs offering better loan forgiveness prospects due to their debt. This can steer them towards public sector jobs or specific firms providing loan repayment assistance, potentially deviating from their initially preferred career paths. Law school debt significantly influences career choices, pushing graduates to prioritize high-paying jobs or those with loan forgiveness programs to manage their financial burdens effectively.
The Effect on Career Aspirations
- Public vs. Private Sector: Many graduates consider public sector jobs, like public defenders or government attorneys, for loan forgiveness programs, even if they initially wanted to work in corporate law.
- Entrepreneurship: High debt can deter graduates from starting their own firms due to the financial risk involved.
- Geographic Limitations: Graduates might choose to work in higher-paying markets to manage debt, limiting their location options.
4. What are the Loan Repayment Options for Lawyers with Student Debt?
Lawyers have several loan repayment options, including income-driven repayment plans, standard repayment plans, and loan consolidation. Income-driven repayment plans, such as Income-Based Repayment (IBR) and Pay As You Earn (PAYE), cap monthly payments based on income and family size. These plans can lead to loan forgiveness after a set period, typically 20 to 25 years.
Types of Loan Repayment Plans
| Repayment Plan | Description | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Repayment | Fixed monthly payments over 10 years. | Quickest repayment, lowest total interest paid. | Higher monthly payments. |
| Income-Driven Repayment | Payments based on income and family size, with potential forgiveness after 20-25 years. | Lower monthly payments, potential for loan forgiveness. | Longer repayment period, higher total interest paid, taxes on forgiven amount. |
| Graduated Repayment | Payments start low and increase every two years over 10 years. | Lower initial payments. | Higher total interest paid, may not be suitable for those with limited income growth. |
| Loan Consolidation | Combines multiple federal loans into one loan with a weighted average interest rate. | Simplifies repayment, may qualify for certain repayment plans. | May lose benefits on original loans, such as interest rate discounts. |
Benefits of Income-Driven Repayment Plans
- Lower Monthly Payments: Payments are adjusted based on income, making them more manageable.
- Potential Loan Forgiveness: After 20-25 years of qualifying payments, the remaining balance may be forgiven.
5. What are the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) Program Requirements?
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments made under a qualifying repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer. Qualifying employers include government organizations, non-profits, and certain other public service organizations. This program is a lifeline for lawyers working in public interest roles.
Eligibility Criteria for PSLF
- Qualifying Employer: Must be employed by a government organization (federal, state, local, or tribal) or a non-profit organization that is tax-exempt under Section 501(c)(3) of the Internal Revenue Code.
- Qualifying Loan: Only Direct Loans are eligible. Other federal student loans, such as Federal Family Education Loan (FFEL) Program loans, are not eligible unless consolidated into a Direct Consolidation Loan.
- Qualifying Repayment Plan: Must be repaying loans under an income-driven repayment plan.
- Qualifying Payments: Must make 120 qualifying monthly payments while working full-time for a qualifying employer.
Steps to Apply for PSLF
- Confirm Eligibility: Ensure employment qualifies and loans are Direct Loans.
- Submit Employment Certification Forms: Annually submit the Employment Certification for Public Service Loan Forgiveness form to the U.S. Department of Education to verify qualifying employment.
- Make Qualifying Payments: Ensure timely payments under a qualifying repayment plan.
- Apply for Forgiveness: After making 120 qualifying payments, submit the application for Public Service Loan Forgiveness.
6. How Can Lawyers Effectively Manage Their Student Loan Debt?
Effective management of student loan debt involves creating a budget, understanding repayment options, and exploring loan forgiveness programs. Consider refinancing options to secure lower interest rates and explore additional income streams to accelerate repayment. Financial planning and proactive management are key to alleviating the burden of law school debt.
Strategies for Effective Debt Management
- Budgeting: Create a detailed budget to understand income and expenses, allowing for informed decisions about loan repayment.
- Refinancing: If eligible, refinance student loans to potentially lower the interest rate.
- Debt Consolidation: Consolidate federal loans to simplify repayment and potentially access more favorable terms.
- Financial Planning: Consult with a financial advisor to develop a long-term financial plan that includes student loan repayment.
- Side Hustles: Explore additional income streams to allocate more funds towards loan repayment.
7. What are the Tax Implications of Student Loan Forgiveness for Lawyers?
Student loan forgiveness can have tax implications. While some forgiveness programs, like PSLF, are tax-free, others, such as those under income-driven repayment plans, may be considered taxable income by the IRS. It’s crucial to understand these implications and plan accordingly.
Understanding Taxable Income
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF): Generally tax-free under current IRS regulations.
- Income-Driven Repayment Forgiveness: The forgiven amount may be considered taxable income, potentially increasing your tax liability in the year the forgiveness is granted.
Strategies to Mitigate Tax Liabilities
- Plan Ahead: Consult with a tax professional to estimate potential tax liabilities.
- Adjust Withholding: Adjust tax withholding to account for potential tax liabilities.
- Save for Taxes: Set aside funds to cover the potential tax liability.
8. What Resources are Available to Help Lawyers Manage Student Debt?
Various resources are available to help lawyers manage student debt, including financial advisors, online calculators, and educational programs offered by bar associations and law schools. These resources provide valuable guidance on repayment options, budgeting, and financial planning. At internetlawyers.net, we also offer resources and connections to legal professionals who can provide advice.
Helpful Resources for Lawyers
- American Bar Association (ABA): Offers resources and programs related to student loan debt management.
- Law School Financial Aid Offices: Provides counseling and resources on loan repayment options.
- Financial Advisors: Offers personalized advice on debt management and financial planning.
- Online Student Loan Calculators: Helps estimate monthly payments and repayment timelines.
9. How Do Law School Rankings Correlate with Student Debt?
Law schools with higher rankings often have higher tuition costs, leading to greater student debt. However, graduates from top-ranked schools may also have better job prospects and higher earning potential, which can help them manage their debt more effectively. Balancing the cost of education with potential career outcomes is crucial.
Debt vs. Earning Potential
| Law School Category | Average Tuition | Average Debt | Potential Salary |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top 10 | $60,000+ | $150,000+ | $180,000+ |
| Private | $40,000+ | $130,000+ | $100,000+ |
| Public (In-State) | $25,000+ | $80,000+ | $70,000+ |
10. How Can I Minimize Law School Debt Before, During, and After Law School?
To minimize law school debt, focus on securing scholarships and grants, reducing living expenses, and working part-time during school. After graduation, prioritize high-paying jobs or those offering loan repayment assistance. Careful planning and financial discipline can significantly reduce the burden of student loans.
Practical Steps to Minimize Debt
- Before Law School:
- Apply for scholarships and grants.
- Save money to reduce borrowing needs.
- Consider attending a more affordable law school.
- During Law School:
- Minimize living expenses by budgeting carefully.
- Work part-time to offset costs.
- Avoid unnecessary spending.
- After Law School:
- Prioritize high-paying jobs.
- Explore loan repayment assistance programs.
- Make extra payments on loans when possible.
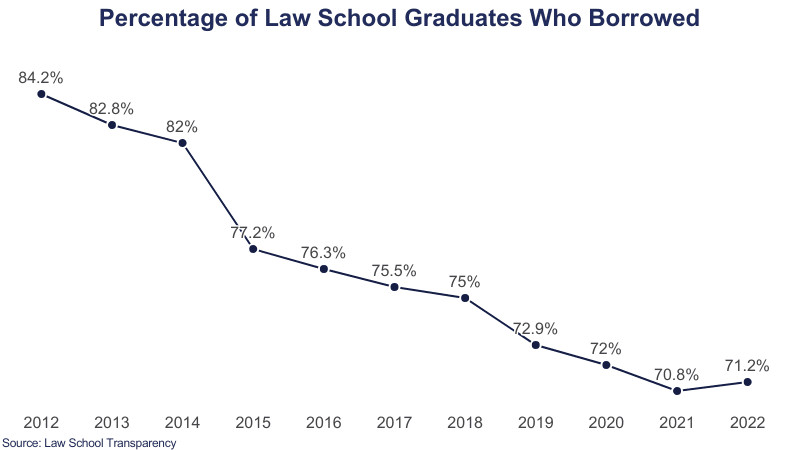 Average law school debt graphic 2 on Education Data Initiative
Average law school debt graphic 2 on Education Data Initiative
11. What Are the Latest Trends in Law School Tuition and Debt?
Recent trends indicate that law school tuition continues to rise, albeit at a slower pace due to increased awareness and efforts to control costs. Student debt remains a significant issue, with law schools and bar associations focusing on providing more resources for financial planning and debt management.
Current Trends in Law School Finances
- Tuition Increases: Tuition continues to rise, but some schools are implementing measures to control costs.
- Debt Management Resources: Law schools and bar associations are offering more resources to help students manage debt.
- Scholarship Opportunities: There is a growing emphasis on providing more scholarship opportunities to reduce the burden of debt.
- Online Education: Online law programs may offer more affordable options for some students.
12. What are the Common Misconceptions About Law School Debt?
One common misconception is that a law degree guarantees a high-paying job that can easily cover student loan debt. While some lawyers earn high salaries, many others, particularly those in public service or small firms, struggle to manage their debt. Another misconception is that loan forgiveness is a simple solution, but it often comes with strict requirements and potential tax implications.
Addressing Misconceptions
- Myth: A law degree guarantees a high-paying job.
- Reality: Job prospects and salaries vary widely depending on the school, location, and type of legal work.
- Myth: Loan forgiveness is easy to obtain.
- Reality: Loan forgiveness programs have strict requirements and may not be available to everyone.
- Myth: All lawyers can easily manage their student debt.
- Reality: Many lawyers, especially those in public service, face significant challenges in managing their debt.
13. How Does Law School Debt Differ Across Demographics?
Student loan debt among law school graduates varies significantly across demographics. Black or African American graduates often have higher debt loads compared to their white counterparts due to factors such as income disparities and access to financial resources. According to the American Bar Association (ABA), women and minority law school graduates bear a disproportionate percentage of student debt, largely due to income disparities.
Demographic Disparities in Law School Debt
| Demographic Group | Average Debt | Factors Contributing to Higher Debt |
|---|---|---|
| Black/African American | Higher | Income disparities, limited access to resources |
| Hispanic/Latino | Higher | Income disparities, limited access to resources |
| Women | Similar | Income disparities after graduation |
Addressing Disparities
- Scholarship Programs: Targeted scholarship programs for underrepresented groups can help reduce debt.
- Financial Literacy Programs: Financial literacy programs can help students make informed decisions about borrowing.
- Mentorship Programs: Mentorship programs can provide guidance and support to students from diverse backgrounds.
14. What are the Alternatives to Traditional Law School to Avoid Debt?
Alternatives to traditional law school to avoid debt include attending part-time programs, choosing more affordable law schools, and exploring accelerated programs. Some students also consider paralegal roles or other legal professions that do not require a law degree but still offer opportunities in the legal field.
Alternative Pathways in the Legal Field
- Part-Time Programs: Allows students to work while attending law school, reducing the need to borrow.
- Affordable Law Schools: Public law schools and those in lower-cost areas can significantly reduce tuition expenses.
- Paralegal Roles: Offers opportunities to work in the legal field without the cost of law school.
- Legal Tech: Explore roles in legal technology, which may not require a law degree but offer opportunities in the legal sector.
15. How Can Current Law Students Prepare for Loan Repayment After Graduation?
Current law students can prepare for loan repayment by understanding their repayment options, creating a budget, and seeking advice from financial advisors. They should also research potential employers and evaluate their loan repayment assistance programs. According to Vanderbilt law school graduates have the lowest salary-to-debt ratio out of law schools, with a ratio of 1.36 to 1, highlighting the importance of considering salary-to-debt ratios when choosing a law school.
Preparing for Loan Repayment
- Understand Repayment Options: Familiarize yourself with income-driven repayment plans, standard repayment plans, and loan consolidation.
- Create a Budget: Develop a budget to understand your income and expenses.
- Seek Financial Advice: Consult with a financial advisor to develop a personalized repayment plan.
- Research Employers: Investigate potential employers and their loan repayment assistance programs.
16. What are Some Strategies for Paying Off Law School Debt Faster?
Strategies for paying off law school debt faster include making extra payments, refinancing to a lower interest rate, and increasing income through side hustles or additional employment. Consider the avalanche or snowball method to prioritize paying off high-interest loans first.
Accelerated Debt Repayment Strategies
- Make Extra Payments: Allocate additional funds to pay down the principal balance.
- Refinance Loans: Refinance to a lower interest rate to reduce the total amount paid over time.
- Increase Income: Pursue side hustles or additional employment to generate more income for loan repayment.
- Avalanche or Snowball Method: Prioritize paying off high-interest loans first (avalanche) or the smallest loans first (snowball).
17. What Role Does Financial Literacy Play in Managing Law School Debt?
Financial literacy is crucial for managing law school debt. Understanding interest rates, repayment options, and budgeting principles can empower lawyers to make informed financial decisions and avoid common pitfalls. Law schools and bar associations are increasingly recognizing the importance of financial literacy and offering related programs.
The Importance of Financial Literacy
- Informed Decision-Making: Financial literacy helps lawyers make informed decisions about borrowing and repayment.
- Budgeting Skills: Understanding budgeting principles allows for effective management of income and expenses.
- Avoiding Pitfalls: Financial literacy can help lawyers avoid common mistakes, such as defaulting on loans.
18. How Can the Legal Profession Support Lawyers Burdened by Student Debt?
The legal profession can support lawyers burdened by student debt by advocating for loan forgiveness programs, promoting financial literacy, and providing mentorship opportunities. Law firms can also offer loan repayment assistance programs to attract and retain talent.
Supporting Lawyers with Student Debt
- Advocate for Loan Forgiveness: Support policies that expand and improve loan forgiveness programs.
- Promote Financial Literacy: Offer financial literacy programs through law schools and bar associations.
- Provide Mentorship: Connect young lawyers with experienced professionals who can offer guidance on debt management.
- Loan Repayment Assistance: Law firms can offer loan repayment assistance programs.
19. What is the Impact of Law School Debt on Lawyers’ Mental Health and Well-Being?
Law school debt can significantly impact lawyers’ mental health and well-being, leading to stress, anxiety, and depression. The financial pressure of managing debt can affect personal relationships, career satisfaction, and overall quality of life. Addressing the mental health challenges associated with law school debt is crucial for promoting a healthy and sustainable legal profession.
Mental Health Challenges
- Stress and Anxiety: The burden of debt can lead to chronic stress and anxiety.
- Depression: Financial pressure can contribute to feelings of hopelessness and depression.
- Impact on Relationships: Stress related to debt can strain personal relationships.
Strategies for Promoting Well-Being
- Mental Health Resources: Access mental health resources and support services.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practice stress management techniques, such as mindfulness and exercise.
- Financial Counseling: Seek financial counseling to develop a plan for managing debt.
20. How Does the Cost of Law School in the U.S. Compare to Other Countries?
The cost of law school in the U.S. is among the highest in the world. Tuition fees in other countries, such as Canada, the UK, and Europe, are often significantly lower, and some countries offer free or heavily subsidized education to domestic and international students. This makes studying law in the U.S. a substantial financial commitment compared to other options.
Cost Comparison
| Country | Average Tuition | Additional Information |
|---|---|---|
| United States | $40,000+ | High tuition fees, significant student debt. |
| Canada | $10,000 – $20,000 | Lower tuition fees compared to the U.S., various funding options. |
| United Kingdom | $12,000 – $25,000 | Lower tuition fees compared to the U.S., government support for domestic students. |
| Europe (Germany) | $0 – $10,000 | Free or heavily subsidized education for domestic and international students. |
Conclusion
Navigating law school debt requires a proactive and informed approach. By understanding the various repayment options, loan forgiveness programs, and debt management strategies, lawyers can alleviate the financial burden and focus on their careers. Internetlawyers.net is dedicated to providing resources and support to help legal professionals manage their debt effectively.
For personalized advice and assistance with legal matters, including debt management, contact us at:
Address: 111 Broadway, New York, NY 10006, United States
Phone: +1 (212) 555-1212
Website: internetlawyers.net
FAQ: Managing Law School Debt
1. What is the average student loan debt for a lawyer after graduation?
The average student loan debt for a lawyer after graduation is approximately $130,000, according to recent statistics. This figure includes both undergraduate and law school loans.
2. How can I lower my monthly student loan payments as a lawyer?
Lawyers can lower their monthly student loan payments by enrolling in income-driven repayment (IDR) plans, which base payments on income and family size, potentially leading to loan forgiveness after 20-25 years.
3. What is the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program, and am I eligible?
The Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program forgives the remaining balance on Direct Loans after 120 qualifying monthly payments made under a qualifying repayment plan while working full-time for a qualifying employer, such as a government or non-profit organization.
4. How do I apply for the Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) program?
To apply for PSLF, submit the Employment Certification for Public Service Loan Forgiveness form annually to the U.S. Department of Education to verify qualifying employment, and after making 120 qualifying payments, submit the application for Public Service Loan Forgiveness.
5. What are the tax implications of student loan forgiveness for lawyers?
While Public Service Loan Forgiveness (PSLF) is generally tax-free, forgiveness under income-driven repayment plans may be considered taxable income by the IRS, potentially increasing your tax liability in the year the forgiveness is granted.
6. Can I refinance my student loans to get a lower interest rate?
Yes, you can refinance your student loans to potentially lower the interest rate, but consider the trade-offs, as refinancing federal loans into private loans means losing access to federal income-driven repayment plans and forgiveness programs.
7. What are the best strategies for paying off law school debt faster?
Strategies for paying off law school debt faster include making extra payments, refinancing to a lower interest rate, and increasing income through side hustles or additional employment.
8. How does law school debt affect career choices for new lawyers?
Law school debt often influences career choices, with many graduates prioritizing high-paying jobs or those offering loan repayment assistance programs to manage their financial burdens effectively.
9. What resources are available to help lawyers manage their student loan debt?
Resources available to help lawyers manage student loan debt include financial advisors, online calculators, and educational programs offered by bar associations and law schools, as well as resources provided by internetlawyers.net.
10. Is law school still worth it considering the high cost of tuition and debt?
The value of law school depends on individual career goals and financial circumstances, but it can be worth it for those passionate about law and willing to manage their debt strategically through informed financial planning and career choices.

